marigolds pdf
Get your free Marigolds PDF download. Explore the vibrant world of marigolds with our comprehensive guide. Perfect for gardening enthusiasts!
Marigolds, vibrant flowers known for their bright yellow and orange hues, are often called “herb of the sun” due to their strong connection to sunlight. Scientifically classified as Tagetes spp., they are widely cultivated for their beauty, versatility, and cultural significance. These flowers are not only popular in gardens but also hold importance in traditional rituals, skincare, and natural dyes, making them a multifaceted plant with diverse applications.
1.1 Overview of Marigolds
Marigolds are vibrant, sun-loving flowers known for their bright yellow and orange hues, often used in gardens and floral arrangements. Belonging to the Tagetes genus, they are native to the Americas and thrive in well-drained soil. Their strong, pungent scent deters pests, making them a practical choice for gardeners seeking natural pest control and aesthetic appeal.
1.2 Importance of Marigolds in Gardens and Culture
Marigolds are cherished for their vibrant blooms and versatility in gardens, adding color and vitality. Culturally, they symbolize warmth, renewal, and celebration, featuring prominently in festivals like Mexico’s Day of the Dead. Their ability to repel pests and attract pollinators makes them invaluable in sustainable gardening practices, enhancing both beauty and biodiversity in outdoor spaces.
Botanical Profile of Marigolds
Marigolds, belonging to the Tagetes genus, are annual or perennial plants native to the Americas. They are characterized by their bright, pom-pom-like flowers and strong, pungent scents, with species varying in size and color. Their robust growth and adaptability make them a popular choice for gardens worldwide.
2.1 Scientific Classification and Species
Marigolds belong to the Tagetes genus, within the sunflower tribe of the daisy family (Asteraceae). The most common species include Tagetes erecta (African marigold), Tagetes patula (French marigold), and Tagetes tenuifolia (signet marigold). These species vary in size, flower structure, and color, offering diverse options for cultivation and use in various applications.
2.2 Physical Characteristics and Growth habits
Marigolds are annual plants with bright yellow to orange flowers, typically growing between 20-90 cm tall. Their leaves are fern-like or lance-shaped, with a strong, pungent scent. Thriving in well-drained soil and full sun, they are drought-tolerant and easy to cultivate, making them ideal for gardens and containers, blooming profusely from summer to fall.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Marigolds hold deep cultural and historical value, often used in traditional rituals, festivals, and as symbols of remembrance. They represent both grief and celebration across various cultures, embodying their versatility and enduring significance in human history and spiritual practices.
3.1 Symbolism and Meaning in Different Cultures
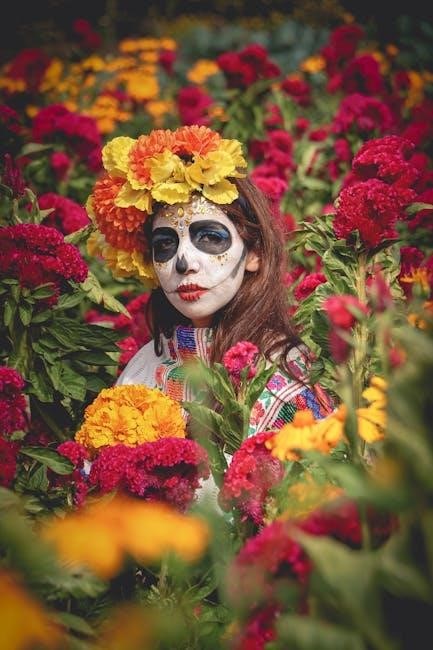
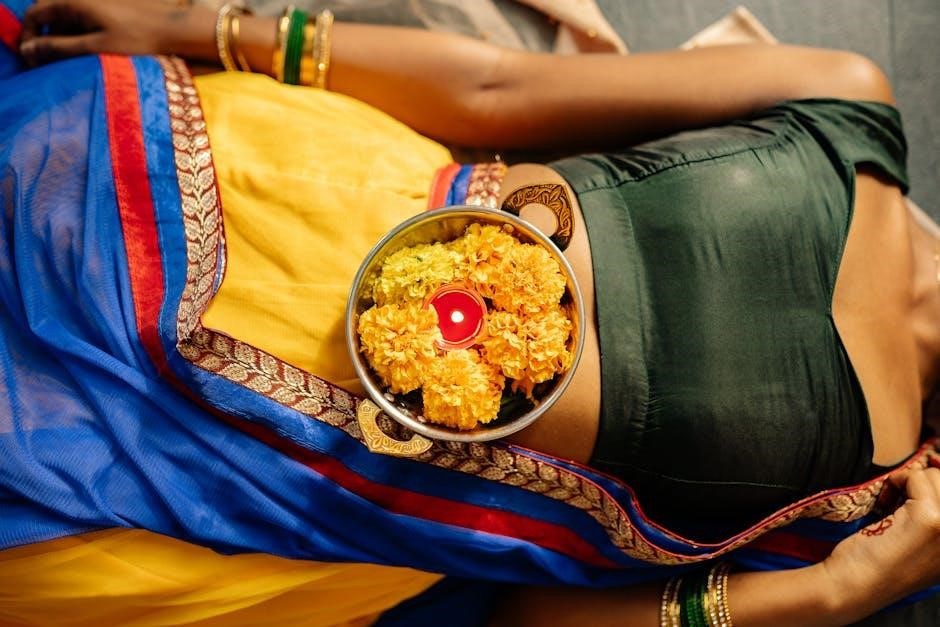
Marigolds symbolize diverse meanings across cultures. In Mexico, they’re central to Día de los Muertos, guiding spirits with their bright hues. In India, they’re used in weddings and religious rituals, symbolizing prosperity and sacredness. In Western cultures, they often represent creativity and warmth, while their strong scent and vibrant colors carry symbolic significance globally.
3.2 Historical Uses of Marigolds
Marigolds have been used historically in traditional medicine, rituals, and as natural dyes. Ancient Mexicans and Aztecs used them in ceremonial offerings and for healing. In Europe, they were adopted for culinary purposes and as a remedy for indigestion; Their vibrant flowers also symbolized prosperity and protection in various cultural practices.
3.3 Marigolds in Traditional Festivals and Rituals
Marigolds are integral to various cultural celebrations, notably Mexico’s Day of the Dead, where orange marigolds guide spirits. In India, they adorn festivals like Pongal, symbolizing prosperity and renewal, while in other traditions, their bright hues are used to honor ancestors and celebrate seasonal change with vibrant displays and rituals.

Marigolds in Gardening
Marigolds are popular garden flowers due to their easy growth, vibrant colors, and pest-repellent properties. They thrive in sunny, well-drained areas and are often used in companion planting to protect crops like tomatoes from nematodes, enhancing garden health and biodiversity with minimal maintenance required.
4.1 How to Grow and Care for Marigolds
Marigolds thrive in sunny locations with well-drained soil. Plant seeds 1-2 inches deep in spring or fall. Water regularly during growth, but avoid overwatering once established. Fertilize lightly for vibrant blooms. Deadhead spent flowers to encourage continuous flowering. These low-maintenance plants are ideal for borders, containers, and companion planting, repelling pests naturally.
4.2 Pest and Disease Management
Marigolds are resilient but can be susceptible to nematodes, aphids, and powdery mildew. Use natural repellents like neem oil or garlic sprays to deter pests. Practice crop rotation and ensure good air circulation to prevent fungal diseases. Regularly inspect plants and remove infected areas to maintain healthy growth and vibrant blooms throughout the season.
4.3 Companion Planting with Marigolds
Marigolds repel nematodes, whiteflies, and other pests, making them ideal companions for tomatoes, peppers, and carrots. Their bright flowers also attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and bees. Plant marigolds alongside herbs such as basil and rosemary to enhance growth and deter pests, creating a balanced and thriving garden ecosystem naturally.
Health and Wellness Benefits
Marigolds possess medicinal properties, offering anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial benefits. Their extracts are used in skincare for wound healing and soothing irritation, promoting overall well-being naturally.
5.1 Medicinal Properties of Marigolds
Marigolds, particularly Calendula officinalis, are renowned for their anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. They contain flavonoids and triterpenoids, which aid in healing wounds, soothing skin irritations, and reducing inflammation. Traditionally, marigold extracts have been used to treat minor injuries, eczema, and digestive issues, making them a valuable natural remedy in herbal medicine.
5.2 Marigold Extracts and Their Uses
Marigold extracts, rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, are widely used in skincare products, pharmaceuticals, and natural remedies. They soothe skin irritations, reduce inflammation, and promote wound healing. These extracts also find applications in traditional medicine for pain relief and as a natural remedy for digestive and respiratory issues.
5.3 Skincare and Cosmetic Applications
Marigold extracts are prized in skincare for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which soothe irritations and protect against environmental stressors. They are used in creams, serums, and ointments to promote healing, reduce redness, and enhance skin elasticity, making them a popular ingredient in natural and organic cosmetic products for various skin types.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Marigolds enhance soil health by repelling pests and attracting beneficial insects, reducing the need for pesticides. Their bright flowers also support pollinators, fostering biodiversity in ecosystems.
6.1 Soil Health and Pest Control
Marigolds significantly improve soil health by repelling nematodes and pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Their strong roots also break up compacted soil, enhancing aeration and nutrient absorption. Additionally, their pungent scent deters pests, creating a natural barrier that protects neighboring plants, thus promoting a balanced and healthy garden ecosystem.
6.2 Pollinator Attraction and Biodiversity
Marigolds attract pollinators like bees and butterflies with their vibrant blooms, enhancing biodiversity. Their nectar-rich flowers support pollinator health, fostering garden ecosystems. This makes them ideal for promoting ecological balance and supporting beneficial insects in sustainable gardening practices.
6.3 Marigolds as Natural Dyes
Marigolds are a rich source of natural pigments, particularly carotenoids, which are used to create vibrant dyes. Their bright yellow and orange hues are extracted from the flowers and utilized in textiles, food coloring, and cosmetics. This sustainable practice offers an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic dyes, promoting environmental conservation and natural resource utilization.

Culinary Uses of Marigolds
Marigolds add a vibrant touch to culinary creations. Their edible flowers can be used in salads, as a natural food coloring, and to make herbal teas.
7.1 Edible Flowers and Recipes
Marigold flowers are edible and often used in culinary dishes. Their bright petals add color and flavor to salads, soups, and sauces. They can be used as a natural dye or garnish. Incorporating marigold flowers into recipes enhances both visual appeal and nutritional value, making them a versatile ingredient for creative cooking.
7.2 Marigold Tea and Infusions
Marigold flowers can be steeped to make a soothing tea, offering potential health benefits. The infusion is known for its calming properties and mild floral flavor. It is often consumed for its antioxidant content and to support digestive health. Marigold tea is a popular choice in herbal blends, appreciated for its gentle, cleansing effects.
7.3 Food Coloring and Garnishing
Marigold flowers are used as natural food colorants, adding vibrant hues to dishes like soups, sauces, and rice. Their petals, fresh or dried, serve as garnishes, enhancing visual appeal in salads and desserts. Marigold-infused oils and butters also add color and subtle floral flavors, making them versatile in culinary applications.
Marigolds in Art and Literature
Marigolds often symbolize warmth and creativity in art, featured in vibrant still-life paintings and cultural motifs. In literature, they appear as metaphors for love, renewal, and resilience, enriching poetic imagery and storytelling.
8.1 Depictions in Art and Symbolism
Marigolds are frequently depicted in art as symbols of warmth and vitality. Their bright hues and robust forms inspire still-life compositions, while their symbolic meanings, such as renewal and remembrance, are often highlighted in cultural and religious imagery, making them a popular motif in both traditional and contemporary artistic expressions.
8.2 Literary References and Poetic Imagery
Marigolds often appear in literature as symbols of life’s vibrancy and fleeting beauty. In Mexican culture, they feature prominently in Day of the Dead imagery, representing the spirit world. Poets worldwide use marigolds as metaphors for renewal, resilience, and the transient nature of life, drawing inspiration from their radiant colors and enduring presence.
8.4 Marigolds in Folklore and Myths
Marigolds hold deep symbolic meaning in folklore, often representing the bridge between life and death. In Mexican culture, they guide spirits during the Day of the Dead. In Hindu mythology, marigolds are linked to sacred rituals, warding off negativity and symbolizing divine protection. Their vibrant hues embody the essence of spiritual renewal and connection.

Marigolds in Modern Science
Modern science explores marigolds for their medicinal properties, biotechnological potential, and environmental applications. Research focuses on their antimicrobial compounds, hybridization for improved traits, and sustainable uses in agriculture and industry.
9.1 Research on Marigold Compounds
Research on marigold compounds focuses on extracting bioactive molecules like carotenoids and lutein, which offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies utilize advanced chromatography and spectroscopy to isolate these compounds, exploring their potential in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and skincare products. Such investigations highlight marigolds’ versatility in modern scientific applications.
9.2 Biotechnology and Hybridization
Biotechnology has enabled the creation of hybrid marigold varieties with enhanced traits like vibrant colors and robust growth. Tissue culture techniques and genetic engineering are used to develop disease-resistant strains. Hybridization focuses on crossbreeding species to produce unique flower sizes, colors, and pest resistance, expanding their ornamental and industrial applications significantly.
9.3 Studies on Antimicrobial Properties
Research highlights marigold extracts’ antimicrobial properties, effective against bacteria like E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus. These compounds inhibit microbial growth, showing potential in wound healing and natural preservatives. Studies focus on optimizing extraction methods to enhance potency, offering eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic antibiotics.

Marigolds in Commerce and Industry
Marigolds are valued in commerce for their use in cosmetics, natural dyes, and pharmaceuticals. Their extracts are traded globally, supporting various industries and economies.
10.1 The Marigold Market and Trade
The global marigold market is growing, driven by increasing demand for natural dyes, cosmetics, and herbal products. Key regions include Asia, Europe, and the Americas, with India emerging as a major exporter. Trade involves raw flowers, extracts, and processed products, supported by certifications like organic and fair trade standards.
10.2 Industrial Applications of Marigold Extracts
Marigold extracts are widely used in industries for natural coloring, UV protection, and antimicrobial properties. They serve as eco-friendly dyes in textiles and plastics. Additionally, their carotenoid content enhances food products and cosmetics, while pharmaceutical applications leverage their anti-inflammatory traits, making them a valuable resource across multiple sectors.
10.3 Economic Impact of Marigold Cultivation
Marigold cultivation significantly contributes to local economies by generating revenue through flower and extract sales. Farmers benefit as a cash crop, while processing industries create jobs. The global demand for natural dyes and cosmetics fuels market growth, sustaining livelihoods and fostering economic stability in regions where marigolds are cultivated.
Marigolds, with their enduring appeal, offer versatility in gardening, health, and ecology. Future prospects highlight sustainable practices, innovation, and environmental stewardship, ensuring their continued relevance and value.
11.1 Summary of Key Points
Marigolds are versatile flowers with cultural, ecological, and practical significance. Known for their vibrant colors, they thrive in gardens, symbolize various meanings, and offer benefits like pollinator attraction and pest deterrence. Their adaptability and numerous uses make them a valuable plant for both traditional and modern applications, spanning across health, skincare, and environmental roles.
11.2 Emerging Trends and Innovations
Research advancements in marigold cultivation and biotechnology are driving innovation. AI-driven tools now enable efficient analysis of PDF documents containing marigold data, while hybridization techniques improve flower resilience. These trends highlight the integration of technology and sustainability in modern horticulture, offering promising solutions for future farming practices.
11.3 Conservation Efforts and Sustainability
Efforts to conserve marigold biodiversity focus on sustainable practices like organic farming and eco-friendly extraction methods. Researchers collaborate with farmers to promote non-invasive cultivation techniques, ensuring soil health and resource efficiency. Digital tools aid in monitoring and managing marigold ecosystems, supporting long-term sustainability and environmental balance.